
Then you need to update the kernel initramfs. But I put it here thinking that it may work for someone else since it’s the easiest way out there. Or alternatively install the desired driver selectively: $ sudo apt install nvidia-390Īfter completing the installation, reboot your system. Now run this command in the Ubuntu Terminal to install the NVIDIA driver automatically: $ sudo ubuntu-drivers autoinstall So the above output says that I have NVIDIA Geforce GTX 750 Ti graphic card installed, and the recommended drive to install is nvidia-390.
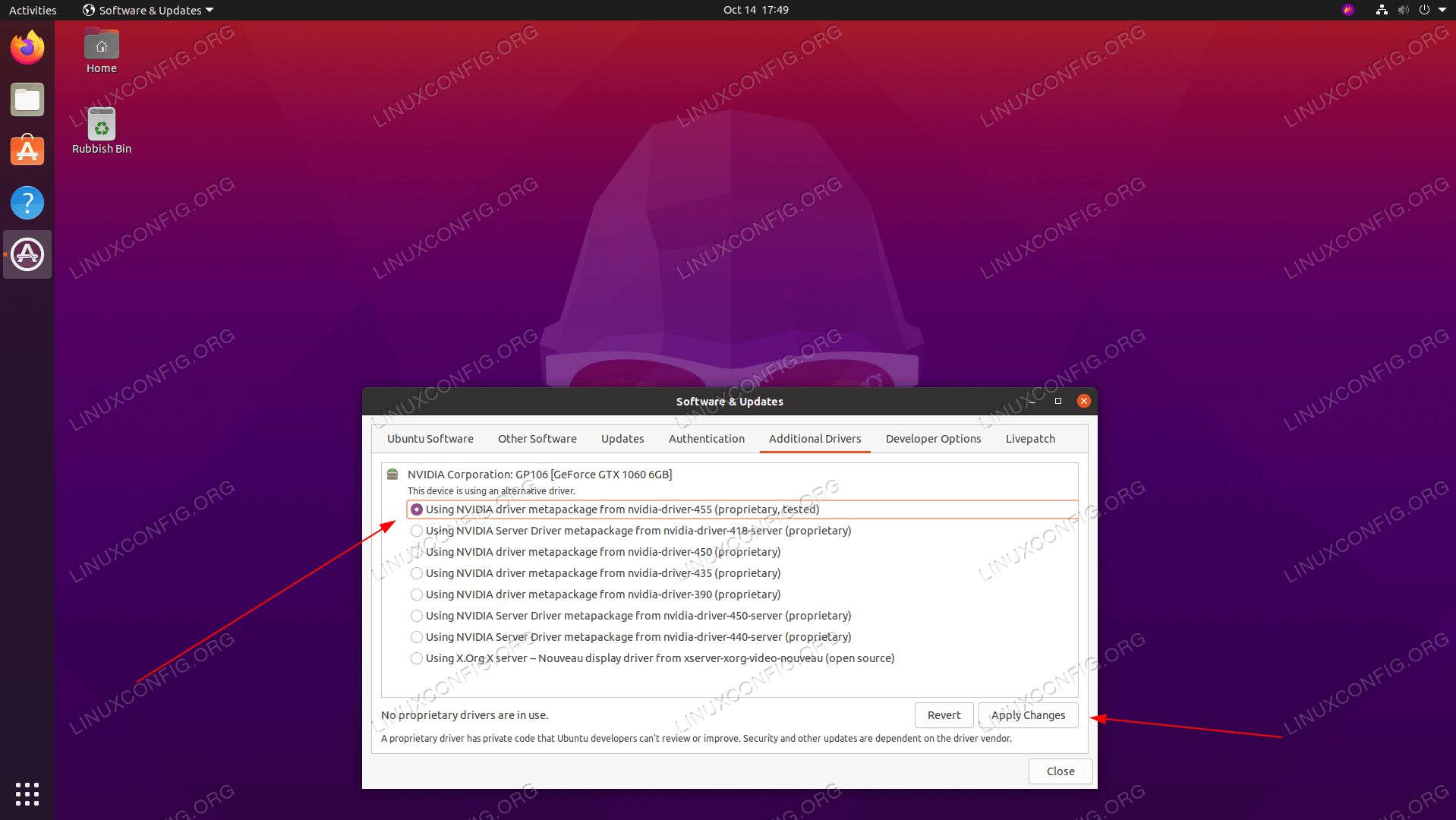
The result will be like this: = /sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:01.0/0000:01:00.0 = modalias : pci:v000010DEd00001380sv00001043sd000084BEbc03sc00i00 vendor : NVIDIA Corporation model : GM107 manual_install: True driver : nvidia-340 - distro non-free driver : nvidia-driver-390 - distro non-free recommended driver : xserver-xorg-video-nouveau - distro free builtin To detect itk, execute this: $ ubuntu-drivers devices $ sudo apt update & sudo apt upgradeįirst we need to detect the model of NVIDIA graphic card and the recommended driver. Use CTRL + ALT + T to open Ubuntu Terminal. If not, then write this command in the terminal. I assume that you’ve updated the system after OS installation. Now I’m writing all the methods that worked for me to fix this problem. So I searched over Google and found some solutions and started applying all until I got my result. My monitor’s resolution is 1368x768, but Ubuntu defaulted it to 960x540. So after proper Linux installation, the first problem I faced was a low-resolution display, which was totally annoying me given that I have a NVIDIA Geforce GTX 750 TI graphics card installed in the machine. Last night I installed Ubuntu 18.04 Bionic Beaver Linux on my desktop PC by completely whipping out Windows 7 OS.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
